- Home Page
- Company Profile
-
Our Products
- BarCode And RFID Hardware
- Labels and Printing Ribbons
- Industrial High-Performance Labels And Tags
- Heat Resistant Labels And Tags
- Tear Resistant And Rip-Proof Tags
- Polyimide PCB Labels
- Wire And Cable Labels
- Tyre Barcode Label
- Sanitaryware Barcode Label
- Security Seal Labels
- Paint Protective Barcode Label
- Gas Cylinder Label Tag
- Barcode Tag And Label for Heat Treatment Process
- Metal Barcode Label And Tag
- RFID Tags And Labels
- System Integration Solutions
- Software Solutions
- Contact Us
X
Product Description
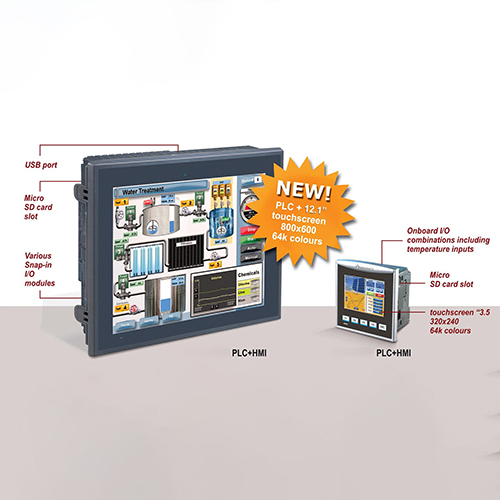
HMI (Human-Machine Interface) and PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) are essential elements in the realm of industrial automation. Below is a concise summary of each component:
PLC (Programmable Logic Controller):
- Purpose: The primary function of a PLC is to manage machinery and processes within industrial environments. It processes inputs and outputs, executes control logic, and makes decisions based on data from sensors.
- Programming: PLCs are generally programmed using methods such as ladder logic, function block diagrams, or structured text.
- Control: They exert direct control over processes by issuing commands to actuators according to the programmed logic.
- Communication: PLCs utilize industrial communication protocols, including Modbus, Profinet, and Ethernet/IP.
HMI (Human-Machine Interface):
- Purpose: An HMI serves as a user-friendly platform for operators to engage with and manage industrial processes. It presents real-time data, facilitates command input, and issues alarms and notifications.
- User Interface: Interaction is achieved through graphics, touch screens, and keypads.
- Function: While it displays process data and enables operators to monitor and manage operations, it does not exert direct control over the processes.
- Communication: HMIs interact with PLCs and other devices through industrial protocols or OPC.
Key Differences:
- Control: PLCs are responsible for controlling processes, whereas HMIs provide the interface for human interaction.
- Complexity: PLCs are more intricate, managing control logic and decision-making, while HMIs are simpler, concentrating on data presentation and user input.
- Hardware: PLCs function as standalone devices, while HMIs may exist as software applications on dedicated hardware or computers.
In conjunction, PLCs and HMIs create a robust framework for industrial automation, promoting efficient and user-friendly management of complex systems.
Are you currently engaged in a specific project or application that incorporates HMI and PLC technology? Contact us today.
Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email